
Maximising Results with GHRP-6 and Ipamorelin Peptide Stacking
Peptide stacking is a sophisticated method that involves the deliberate selection and combination of specific peptides to enhance their individual effects, leading to superior results
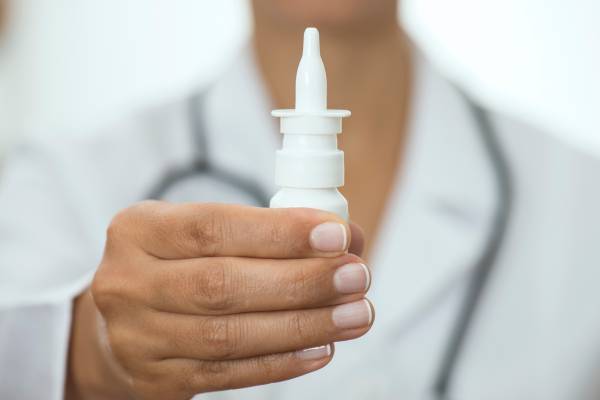
Peptide nasal sprays are emerging as a ground breaking solution in pharmaceuticals, offering a less invasive route for medication administration compared to traditional methods like injections and oral tablets. The nasal mucous membrane, characterised by its high vascularisation and permeability, presents a favourable site for drug absorption, thus facilitating rapid systemic drug delivery. This unique administration route is particularly advantageous for peptide-based drugs, which, due to their molecular size and structure, may not be as effective or stable when administered orally or via other conventional means. United States Researchers have explored various strategies to enhance absorption and efficacy of peptide drugs through intranasal drug delivery.
The potential of peptide nasal sprays extends beyond just the convenience of avoiding injections; it taps into the inherent properties of the nasal mucosa to significantly enhance the bioavailability and effectiveness of therapeutic peptides. Recognising the challenges posed by the nasal route, such as the mucosal barrier and enzymatic degradation, researchers are diligently working on innovative strategies to optimise drug delivery. Among these are the development of cell-penetrating peptides and tight junction modulators, designed to facilitate the transport of peptide drugs across the nasal epithelium. These approaches aim not only to improve drug absorption but also to ensure a sustained and targeted delivery, thereby maximising the therapeutic potential of peptide nasal sprays.
Peptide nasal sprays are increasingly recognised for their ability to offer a non-invasive alternative to traditional drug delivery methods, such as injections. These sprays utilise the nasal route to administer medication directly to the systemic circulation, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract and potential first-pass metabolism in the liver. This route of administration is particularly beneficial for delivering therapeutic peptides, which may have limited oral bioavailability due to degradation in the gastrointestinal tract.
For instance, Semax nasal spray is considered more effective than oral or injectable administration due to its pharmacokinetics and route of delivery. Being a peptide with poor oral bioavailability, Semax is better absorbed through intranasal administration, allowing for direct access to the bloodstream and bypassing the digestive system’s breakdown processes. This direct absorption into the bloodstream via the nasal mucosa enables quicker and more efficient uptake of Semax, leading to enhanced bioavailability and efficacy compared to oral or injectable methods. Consequently, the intranasal route ensures that Semax reaches the brain more rapidly and in higher concentrations, maximizing its cognitive benefits and therapeutic effects as supported by studies
By improving the solubility and stability of peptides, these nasal sprays ensure that an effective dose reaches the systemic circulation, thereby maximising therapeutic outcomes. The integration of absorption enhancers and novel formulation strategies in peptide nasal sprays opens new avenues for the treatment of various diseases, promising a future where non-invasive drug delivery methods are not only feasible but preferred.
The exploration of peptide nasal sprays through United States research studies has significantly advanced our understanding of their potential in medicine, particularly in terms of their efficiency and safety. For instance, the use of cultured human nasal epithelium in research has not only provided a deeper understanding of how therapeutic peptides are absorbed through the nasal mucous membrane but has also offered insights into the challenges and strategies for enhancing drug delivery.
One notable study demonstrated that the intranasal administration of a scavenger peptide could significantly reduce amyloid-β accumulation in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. This finding is profound as it showcases the potential therapeutic applications of peptide nasal sprays in treating neurodegenerative diseases, a field that has been notoriously difficult to address with traditional drug delivery methods.
Moreover, the safety and efficacy of these nasal sprays have been a central focus of research, particularly in the context of treating chronic conditions such as obesity. A study assessing the intranasal peptide YY3-36 highlighted the critical importance of dosage precision and the necessity for rigorous patient monitoring. Despite the innovative approach, the United States study found no significant weight loss in obese patients after 12 weeks of treatment with intranasal PYY3-36, underlining the challenges in achieving desired therapeutic outcomes. This outcome stresses the need for further research to refine dosage strategies and perhaps to explore the combination of peptide nasal sprays with other treatment modalities. It also underscores the crucial role of patient adherence to treatment protocols and the potential impact of individual physiological differences on treatment efficacy.
These studies collectively contribute to a growing body of evidence that, while showing promise, signals the need for continued United States investigation into the optimisation of peptide nasal sprays for various therapeutic applications.
The landscape of pharmaceutical research is ever-evolving, with peptide nasal sprays standing at the forefront of innovative drug delivery systems. Current United States research is rigorously exploring the integration of advanced techniques such as spray freeze-drying and intelligent glucose reaction systems.
These methods aim to significantly enhance the efficiency and safety profiles of peptide nasal sprays by ensuring more precise dosing and improved stability of the peptides. An interesting direction is the development of responsive delivery systems that can adjust the dosage based on real-time glucose levels, thereby offering personalised therapeutic strategies for diabetes management. This approach not only exemplifies the potential for innovation in peptide nasal spray technology but also underscores the importance of addressing specific patient needs through tailored treatment protocols.
Moreover, the exploration of multifaceted drug delivery strategies, which combine various techniques such as nanoparticles, bio-adhesive systems, and cell-penetrating peptides, is gaining traction. These strategies aim to overcome the inherent challenges associated with nasal mucosal absorption, such as low permeability and the proteolytic environment, thereby improving the bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy of peptide drugs. For instance, the use of nanoparticles has shown promise in enhancing the delivery of insulin via nasal sprays, offering a non-invasive alternative to traditional insulin injection therapies.
Such advancements highlight the collaborative efforts required between pharmaceutical scientists and clinicians to not only innovate but also to rigorously validate these new technologies through United States clinical trials. This collaborative approach is vital for ensuring that the developments in peptide nasal spray technologies translate into safe, effective, and patient-friendly treatment options. The synergy between scientific research and clinical application is therefore essential for overcoming the current limitations and unlocking the full potential of peptide nasal sprays in the future.
Direct SARMs United States is committed to this research by providing high purity peptide nasal sprays for clinical investigations.
[1] A comprehensive review of advanced nasal delivery: Specially insulin and calcitonin, European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Volume 192, 1 January 2024, 106630 by Dan Luo, Xiaoqing Ni, Hao Yang et al.
[2] Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Therapeutic Peptides as Nasal Aerosols. Pharmaceutics. 2022 Sep 5;14(9):1870 by Alabsi W, Eedara BB, Encinas-Basurto D, Polt R, Mansour HM.
[3] Efficacy and Safety of Intranasal Peptide YY3–36 for Weight Reduction in Obese Adults, The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, Volume 92, Issue 5, 1 May 2007, Pages 1754–1757, by Ira Gantz, Ngozi Erondu, Madhuja Mallick, Bret Musser, et al.
Disclaimer: We do not supply sarms or peptides to any individual under the age of 21. You must be a licensed and qualified healthcare practitioner. Our team of dedicated professionals are committed to providing an extensive range of products used ONLY in the process of laboratory research by responsible trained and professional individuals. All products listed on this website (direct-sarms.com) and provided through Direct Sarms are intended for laboratory research purposes only. The products listed on this website are NOT for human or animal consumption or ingestion of any kind.

Peptide stacking is a sophisticated method that involves the deliberate selection and combination of specific peptides to enhance their individual effects, leading to superior results
Maximizing Healing and Rejuvenation: Exploring the Benefits of TB500 and GHK-Cu Peptides Combined In the rapidly changing field of biomedical research, peptides have become key
Worldwideshipping

Visa/Mastercard/Zelle
Cryptocurrency /Transfers

Safe and Secure Shopping

We Distribute
From

YOU MUST BE OVER 21 YEARS IN ORDER TO USE THIS WEBSITE. All of the products are to be handled only by properly trained and qualified LABORATORY or RESEARCH professionals.